As we delve into the Frederick Douglass Socratic Seminar Questions, we embark on an intellectual journey that illuminates the life and work of a towering figure in American history. Frederick Douglass, a former slave who became a leading abolitionist, orator, writer, and statesman, left an indelible mark on the fight for equality and social justice.
Through a series of probing questions, this seminar invites us to grapple with Douglass’s complex experiences, ideas, and lasting impact.
Throughout his life, Douglass confronted the horrors of slavery, championed the cause of abolition, and advocated tirelessly for the civil rights of African Americans. His powerful speeches, incisive writings, and unwavering activism shaped the course of American history and continue to inspire generations.
Early Life and Influences
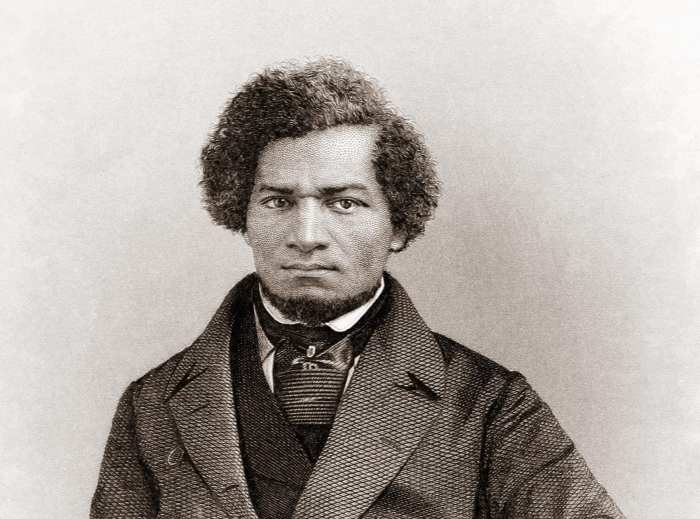
Frederick Douglass’s early experiences as a slave shaped his lifelong fight for freedom and equality. Born into slavery in Maryland in 1818, he endured the brutality and dehumanization of the institution.
Douglass’s quest for education and literacy began at a young age. He secretly taught himself to read and write, an act of defiance that ignited his intellectual curiosity and desire for knowledge. His childhood experiences instilled in him a deep understanding of the injustices faced by enslaved people and fueled his determination to challenge the oppressive system.
Education and Literacy
- Douglass’s self-education was a testament to his resilience and determination.
- Literacy empowered him to communicate his ideas and experiences, giving him a powerful voice in the abolitionist movement.
- Douglass believed that education was essential for African Americans to achieve self-reliance and challenge racism.
Childhood Experiences, Frederick douglass socratic seminar questions
- Douglass’s firsthand experience of slavery gave him a unique perspective on the evils of the institution.
- His memories of being whipped, separated from his family, and denied basic rights shaped his unwavering commitment to abolition.
- Douglass’s childhood experiences instilled in him a deep empathy for all who suffered under oppression.
Abolitionist Movement
Frederick Douglass emerged as a leading voice in the abolitionist movement. He used his powerful speeches and writings to expose the horrors of slavery and advocate for immediate emancipation.
Douglass’s strategies for challenging slavery included public speaking, writing, and political activism. He traveled extensively, delivering speeches that ignited public outrage and challenged prevailing attitudes about race.
Contributions to the Abolitionist Movement
- Douglass’s speeches and writings provided firsthand accounts of the horrors of slavery, debunking the myths and propaganda used to justify the institution.
- He formed alliances with white abolitionists and helped to organize the Underground Railroad, which aided enslaved people in escaping to freedom.
- Douglass’s work played a significant role in galvanizing public support for abolition and contributed to the growing momentum for change.
Impact of Douglass’s Speeches and Writings
- Douglass’s speeches were powerful and persuasive, often drawing large crowds and inspiring listeners to action.
- His writings, including his autobiography, “Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave,” became influential texts in the abolitionist movement.
- Douglass’s work helped to raise awareness about the plight of enslaved people and contributed to the growing demand for an end to slavery.
Reconstruction and Beyond: Frederick Douglass Socratic Seminar Questions

Following the Civil War, Frederick Douglass played a prominent role in the Reconstruction era, advocating for civil rights and suffrage for African Americans.
Douglass’s advocacy extended beyond Reconstruction, as he continued to fight for equality and justice throughout his life. He supported the women’s suffrage movement and spoke out against racial discrimination in all its forms.
Role in the Reconstruction Era
- Douglass was appointed to several government positions during Reconstruction, including the post of Minister Resident and Consul General to Haiti.
- He used his influence to advocate for policies that protected the rights of African Americans, including the 14th and 15th Amendments.
- Douglass’s work helped to establish the foundations for a more just and equitable society.
Challenges and Setbacks
- Despite his efforts, Douglass faced significant challenges during Reconstruction, including the resistance of white supremacists and the failure of the federal government to fully protect the rights of African Americans.
- He witnessed the rise of Jim Crow laws and the resurgence of racial violence, which threatened the progress made during Reconstruction.
- Douglass’s determination remained unwavering, and he continued to fight for equality until his death in 1895.
Legacy and Impact

Frederick Douglass’s life and work left an enduring legacy on American history and the fight for equality.
Douglass’s ideas and activism continue to inspire and influence today, reminding us of the ongoing struggle for justice and the importance of fighting against oppression in all its forms.
Contributions to American History
- Douglass’s autobiography, “Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave,” is a powerful and influential work that provides a firsthand account of the horrors of slavery.
- His speeches and writings helped to shape the abolitionist movement and contribute to the growing demand for an end to slavery.
- Douglass’s advocacy for civil rights and suffrage for African Americans helped to establish the foundations for a more just and equitable society.
Inspiration and Influence
- Douglass’s life and work continue to inspire activists and advocates for social justice today.
- His ideas about freedom, equality, and the power of education resonate with people around the world.
- Douglass’s legacy serves as a reminder of the importance of fighting against oppression and working towards a more just and equitable world.
FAQ Overview
What were Frederick Douglass’s key contributions to the abolitionist movement?
Douglass used his powerful speeches, writings, and personal experiences to expose the horrors of slavery, challenge racist ideologies, and advocate for the immediate emancipation of enslaved people.
How did Douglass’s early life as a slave shape his later beliefs and activism?
Douglass’s firsthand experiences with the brutality and dehumanization of slavery instilled in him a deep understanding of its evils and a lifelong commitment to fighting for freedom and equality.
What were the challenges and setbacks Douglass faced during the Reconstruction era?
Despite his tireless efforts, Douglass encountered resistance from white supremacists and a lack of political will to fully implement Reconstruction policies, which limited his ability to achieve his goals for civil rights and racial equality.