Which of the following molecules has the highest boiling point? This question delves into the fascinating realm of intermolecular forces, molecular weight, molecular structure, hydrogen bonding, and polarity, all of which play a crucial role in determining the boiling point of a substance.
By understanding these factors, we gain valuable insights into the behavior of molecules and their physical properties.
The boiling point of a substance is the temperature at which its vapor pressure equals the pressure surrounding the liquid and the substance changes into a vapor. Various factors influence the boiling point, including the strength of intermolecular forces, molecular weight, molecular structure, hydrogen bonding, and polarity.
This exploration will delve into each of these factors, providing a comprehensive understanding of their impact on the boiling point of molecules.
Intermolecular Forces: Which Of The Following Molecules Has The Highest Boiling Point
Intermolecular forces (IMFs) are the attractive forces that exist between molecules. The strength of these forces determines the boiling point of a substance. The stronger the IMFs, the higher the boiling point.
There are three main types of IMFs:
- Hydrogen bonding: This is the strongest type of IMF and occurs when a hydrogen atom is bonded to a highly electronegative atom, such as oxygen or nitrogen. Hydrogen bonds are responsible for the high boiling points of water, alcohols, and carboxylic acids.
- Dipole-dipole interactions: These occur between molecules that have permanent dipoles. The positive end of one molecule is attracted to the negative end of another molecule. Dipole-dipole interactions are weaker than hydrogen bonds but stronger than van der Waals forces.
- Van der Waals forces: These are the weakest type of IMF and occur between all molecules. Van der Waals forces are due to the attraction between the instantaneous dipoles that are created by the movement of electrons within a molecule.
Molecular Weight
Molecular weight is the sum of the atomic weights of all the atoms in a molecule. The molecular weight of a substance affects its boiling point. In general, the higher the molecular weight, the higher the boiling point.
This is because molecules with higher molecular weights have more electrons and therefore more van der Waals forces. The stronger the van der Waals forces, the higher the boiling point.
| Molecule | Molecular Weight | Boiling Point (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| Helium | 4 | -268.9 |
| Water | 18 | 100 |
| Ethanol | 46 | 78.3 |
| Octane | 114 | 125.7 |
Molecular Structure
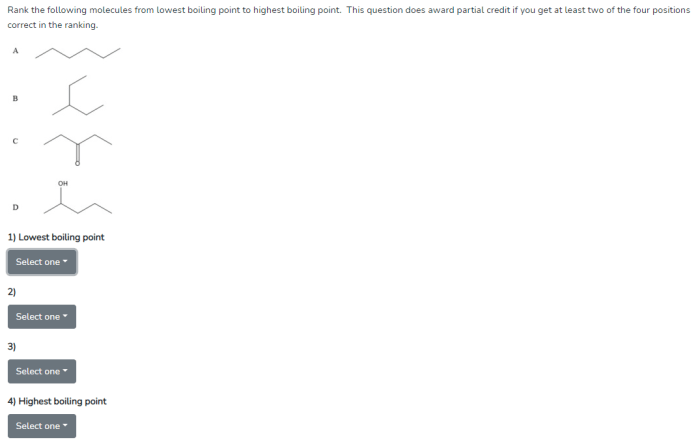
Molecular structure also affects boiling point. Molecules with more complex structures have higher boiling points than molecules with simpler structures.
This is because molecules with more complex structures have more surface area and therefore more van der Waals forces. The stronger the van der Waals forces, the higher the boiling point.
For example, butane has a lower boiling point than pentane, even though pentane has a higher molecular weight. This is because butane has a more compact structure than pentane.
Hydrogen Bonding
Hydrogen bonding is a special type of IMF that occurs when a hydrogen atom is bonded to a highly electronegative atom, such as oxygen or nitrogen. Hydrogen bonds are very strong and can have a significant impact on the boiling point of a substance.
For example, water has a much higher boiling point than methane, even though methane has a higher molecular weight. This is because water molecules can form hydrogen bonds with each other, while methane molecules cannot.
- Water: 100 °C
- Methane: -161.6 °C
Polarity
Polarity is a measure of the uneven distribution of electrons in a molecule. Polar molecules have a positive end and a negative end. The polarity of a molecule affects its boiling point.
In general, polar molecules have higher boiling points than nonpolar molecules. This is because polar molecules can form dipole-dipole interactions with each other. The stronger the dipole-dipole interactions, the higher the boiling point.
| Molecule | Polarity | Boiling Point (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon dioxide | Nonpolar | -78.5 |
| Water | Polar | 100 |
| Ammonia | Polar | -33.3 |
| Methane | Nonpolar | -161.6 |
Popular Questions
What is the relationship between intermolecular forces and boiling point?
Stronger intermolecular forces lead to higher boiling points because more energy is required to overcome these forces and separate the molecules into a vapor.
How does molecular weight affect boiling point?
Heavier molecules tend to have higher boiling points because they have more mass and require more energy to overcome intermolecular forces and vaporize.
What role does molecular structure play in determining boiling point?
Molecules with more complex structures tend to have higher boiling points because their irregular shapes hinder their ability to pack closely together, resulting in weaker intermolecular forces.
How does hydrogen bonding affect boiling point?
Hydrogen bonding is a particularly strong type of intermolecular force that can significantly elevate the boiling point of a substance.
What is the relationship between polarity and boiling point?
Polar molecules have stronger intermolecular forces than nonpolar molecules, leading to higher boiling points.
